As technology advances, so do the methods used to store and analyze data. We’ve seen a shift from centralized processing to distributed computing, and now IoT edge computing is revolutionizing the way we access, process, and analyze data. Edge computing is the practice of utilizing localized resources to store, process, manage, and analyze data. This means that instead of relying on remote servers for data analysis, users can leverage their local devices for quick and secure results. In this blog post, we will explore how IoT edge computing is revolutionizing the future of data analysis. From the benefits of edge computing to current challenges in the industry and more, read on to learn more about why edge computing matters today.
What is IoT Edge Computing?
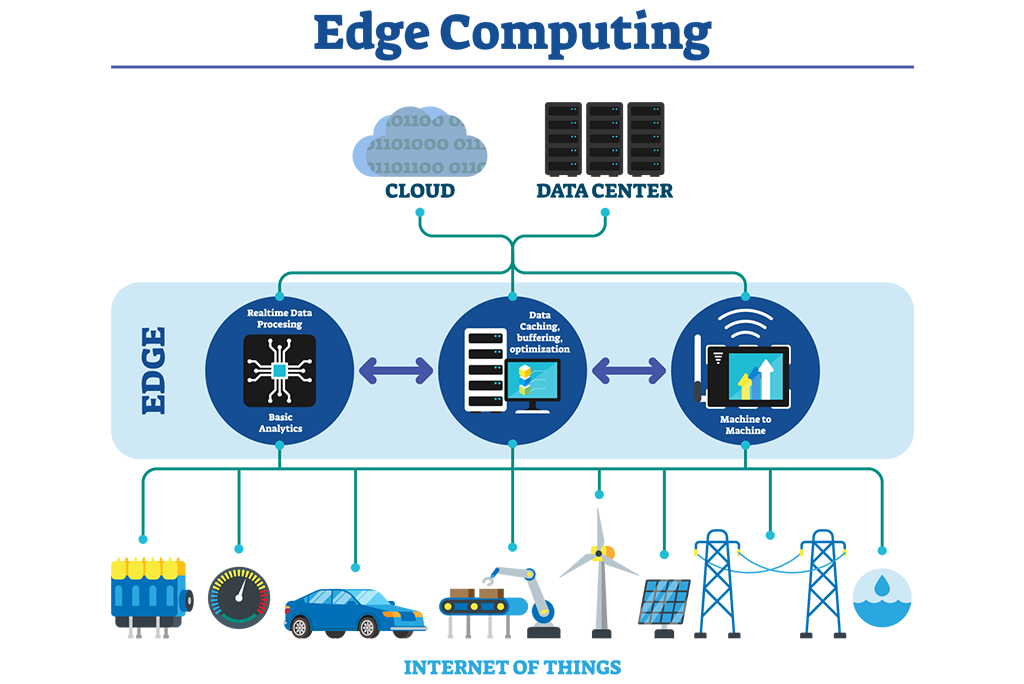
IoT edge computing is a type of computing where data is processed at or near the source of data collection rather than being sent to a central location for processing. This can be done either via an on-device processor or by sending data to a nearby edge server for processing.
The main benefits of IoT edge computing are that it reduces latency, conserves bandwidth, and can enable offline operation. By processing data locally, devices can respond faster to changes and events. This is especially important for time-sensitive applications such as industrial control or augmented reality. In addition, sending less data to the cloud can help reduce network congestion and lower costs. Finally, storing data locally can be helpful in cases where internet connectivity is unreliable or unavailable.
How IoT Edge Computing is Revolutionizing Data Analysis
IoT edge computing is revolutionizing data analysis by allowing organizations to process and analyze data closer to where it is generated. This enables organizations to make faster and more informed decisions based on real-time data, as well as reducing the amount of data that needs to be stored and processed centrally.
Edge computing also has the potential to improve the efficiency of data collection and analysis, as well as reducing costs associated with storing and processing large volumes of data. Additionally, by bringing computation and storage closer to the edge of the network, latency can be reduced, providing a better user experience for applications that require real-time data.
The Benefits of IoT Edge Computing
IoT edge computing is revolutionizing the future of data analysis by making it possible to collect and process data closer to the source of information. This has a number of benefits, including reducing latency, reducing costs, and increasing security.
latency is the time it takes for data to travel from its source to where it is being processed. Reducing latency can have a number of benefits, including reducing the time it takes to make decisions based on data, improving real-time monitoring and control, and reducing bandwith requirements.
costs associated with data collection and processing can be reduced by doing these activities closer to the source of information. In many cases, this also reduces energy consumption as well as the need for expensive infrastructure such as data centers.
collecting and processing data at the edge can also increase security as sensitive data does not need to be transmitted over long distances where it is more vulnerable to interception or attack.
The Challenges of IoT Edge Computing
The internet of things (IoT) refers to the interconnectedness of physical objects and devices, often using sensors, that are able to collect and exchange data. The term “edge computing” describes a model in which data is processed at or near the source of origin, rather than being sent to a central location for processing. IoT edge computing is therefore the intersection of these two technologies, in which data collected by IoT devices is processed at or near the source.
There are a number of challenges associated with IoT edge computing. One challenge is ensuring that data is properly collected and stored by IoT devices. Another challenge is ensuring that the data collected by IoT devices is properly processed and analyzed at the edge. Finally, there are concerns about security and privacy when collecting and processing data from IoT devices.
Despite these challenges, IoT edge computing has the potential to revolutionize the way we collect and analyze data. By processing data at or near the source, we can reduce latency and improve efficiency. Additionally, by processing data locally, we can reduce dependence on centralized infrastructure and make better use of resources.
Conclusion
IoT edge computing is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to transform data analysis and pave the way for more efficient and secure operations. By enabling devices to communicate with each other in real-time, IoT edge computing provides an alternative solution to traditional cloud-based architecture. With its ability to process large volumes of data quickly and securely, this technology can be applied across multiple industries, making it easier than ever before to leverage the power of big data. We look forward to seeing how IoT edge computing will continue to revolutionize the future of data analysis.