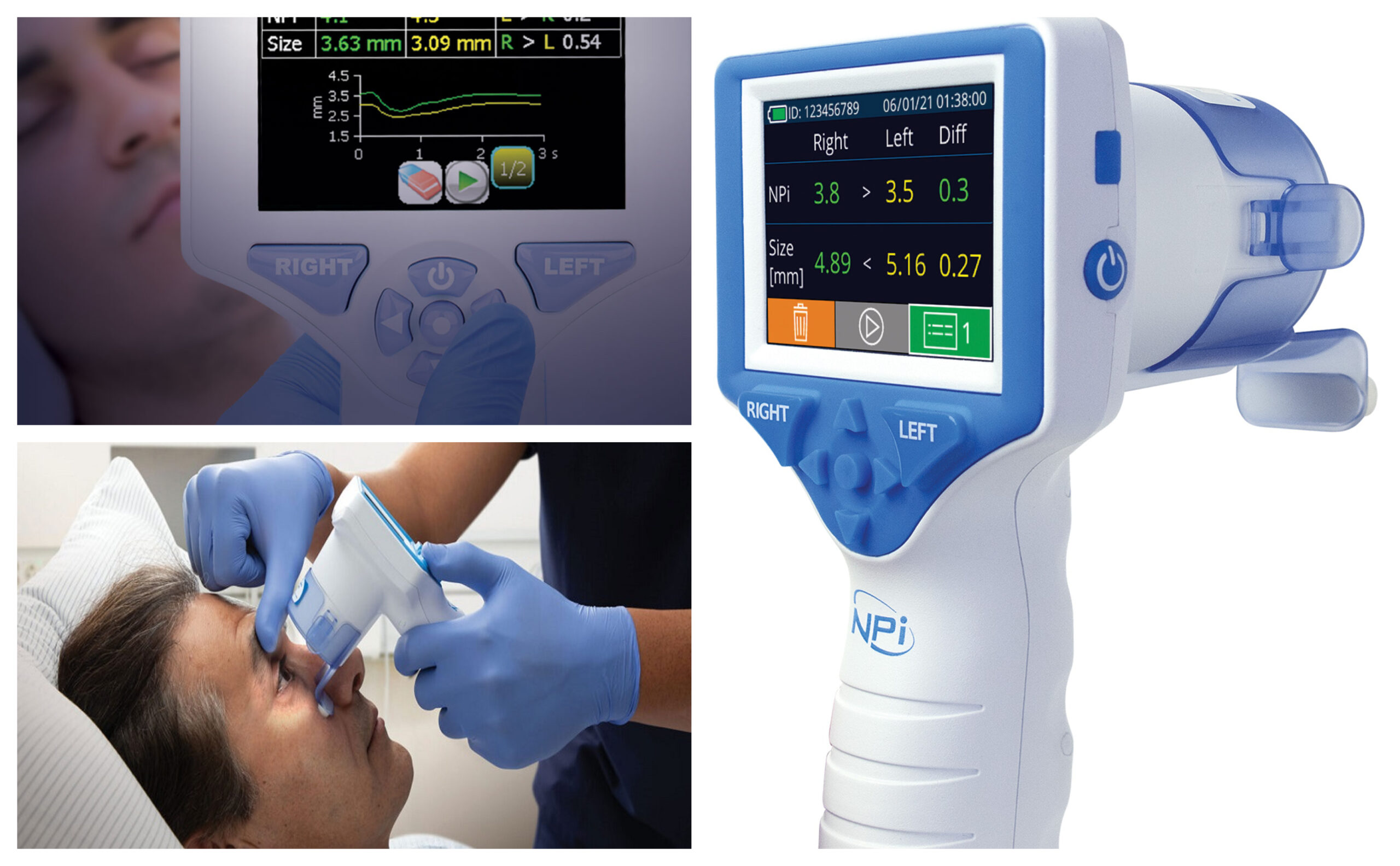
As any medical professional knows, the size of a patient’s pupils can provide valuable insight into their neurological health. Changes in pupil size can be an early indicator of severe conditions such as brain tumors, head injuries, and even certain types of seizures.
Medical professionals must have accurate and reliable tools for measuring pupil size during neurological exams. One such measure is the NPi (neurological pupil index), which calculates the percent change in pupil size. This measure and others can help doctors make more informed decisions about their patients’ care.
But just as important as the tools themselves is understanding the importance of pupil size in neurological exams. By staying informed and up-to-date on the latest measures and techniques, medical professionals can ensure that they provide the best possible care for their patients.
The Role of Pupil Size in Neurological Exams
One of the most important aspects of a neurological exam is measuring pupil size. Changes in pupil size can indicate a range of neurological conditions, including brain injury, brain tumors, and certain eye conditions. Understanding the significance of these changes can help doctors make accurate diagnoses and determine the severity of a patient’s condition.
Measuring Percent Change
One of the critical tools for measuring pupil size is the NPi pupillometer. This device uses infrared technology to accurately measure the size of the pupils in a non-invasive way. Doctors can then use this measurement to calculate the percent change in pupil size, providing valuable information about a patient’s condition.
For example, a patient with a brain injury may have a larger pupil on one side of the face than on the other. This difference in size can indicate the location and severity of the damage. Similarly, a patient with a brain tumor may have a larger pupil size on one side of the face than the other, indicating the tumor’s location.
Other Neurological Tools
You can use other neurological tools to measure pupil size and other aspects of a patient’s condition. For example, an ophthalmoscope can examine the back of the eye and detect any abnormalities. Similarly, a tonometer can measure intraocular pressure and detect diseases such as glaucoma.
So, measuring pupil size is a crucial aspect of neurological exams, and the NPi and other neurological tools are essential for accurate and non-invasive measurement of percent change.With the help of these tools, doctors can make accurate diagnoses and determine the severity of a patient’s condition.
The NPi Measure: What It Is and How It Works?
Regarding neurological exams, pupil size can provide important information about a patient’s condition. The NPi (the neurological pupil index) assesses pupils’ size. It is calculated by dividing the pupil’s diameter by the diameter of the iris.
This number is then multiplied by 100 to give the NPi percentage. The NPi can measure both direct and consensual responses, so medical experts can use it to evaluate the pupils’ response to light in both eyes.
How NPi is Used in Conjunction with Other Measures
Besides the NPi, doctors can use other measures to evaluate pupil size, including the pupillary light reflex, the near reflex, and the accommodation reflex. Health professionals can use these measures with the NPi to give a more comprehensive assessment of the function of the pupils.
For example, doctors can use the pupillary light reflex to test the pupils’ response to light, while medical professionals can use the near reflex to test the pupils’ response to accommodation.
Advantages of Using NPi
One of the main advantages of using the NPi is that it is non-invasive. Unlike other methods of evaluating pupil size, the NPi does not require invasive procedures or equipment. This makes it a safe and easy way to assess the function of the pupils.
Another advantage of the NPi is that doctors and nurses can measure both direct and consensual responses. This means that experts can use it to evaluate the pupils’ response to light in both eyes, which can provide a complete picture of the patient’s condition.
So, the NPi is a valuable measurement for assessing pupil size in a neuro exam. Its non-invasive nature and ability to measure both direct and consensual responses make it a helpful tool for evaluating the percent change in pupil size and providing a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s condition.
Common Neurological Conditions and Pupil Size
Changes in pupil size can indicate certain neurological conditions. It is essential to understand the connection between these conditions and pupil size and how doctors can use the NPi and other measures to evaluate them.
Neurological Conditions
Neurological conditions, such as stroke, brain injury, and multiple sclerosis, can impact pupil sizes. Sometimes, the pupil size can be reduced, while it can be enlarged in others. This can indicate that the brain is not functioning correctly, and it is crucial to be aware of the potential implications.
The NPi and Other Measures
The NPi is a measure that professionals can use to assess changes in pupil size. It is based on the pupil’s reaction to light and can help identify any size changes. Other measures, such as pupillometry, can also measure pupil size.
Evaluating Neurological Conditions
Monitoring pupil size changes make it possible to evaluate neurological conditions. This can help identify potential issues and allow for early intervention. The NPi and other measures can track pupil size changes and help provide a better understanding of the condition.
Understanding the connection between neurological conditions and pupil size cannot be underestimated. Monitoring changes in pupil size makes it possible to identify potential issues and take action. The NPi and other measures can measure the percent change in pupil size and help better understand the condition.
Clinical Applications of Pupil Size Measurements
Pupil size measurements are crucial to neurological exams and can provide valuable insight into a patient’s condition. In clinical settings, pupil size is used to identify issues such as brain tumors, head trauma, and drug toxicity. Doctors can also use it to monitor the progression of certain diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and multiple sclerosis.
Improving Patient Outcomes with NPi and Other Measures
One of the most significant advantages of pupil size measurements is the ability to track percent change over time. The NPi is a measure of the relative constriction of the pupils in response to light, and it is a powerful indicator of brainstem function.
Other tools, such as the pupillometer, can accurately measure pupil size and track changes in real-time. Doctors and other healthcare professionals can use tools like these to improve patient outcomes by identifying and treating issues early on.
Overall, pupil size measurements are a critical aspect of neurological exams, and the pupil exam can help healthcare professionals improve patient outcomes by identifying and treating issues early on. With the help of these tools and measures, doctors can keep a close eye on the progression of diseases and conditions that affect the pupils, ensuring the patients receive the best possible treatment.