India is a historical land where many buildings related to history, many evidences exist. In India, along with the time, the rule and rulers have also been changing. Those who came to India and ruled here and stayed here. Apart from taking a lot from India, these rulers of India have also given a lot to India. From the period of Mahabharata, Ramayana, Rajputs, emperors in the middle and the British rule in the modern period, India has played an important role in making India’s culture, civilization and its historical heritage.
But in all these rulers and times, the most important role has been played by the Mughal rulers in the historical background of India. Who ruled India for the longest time. Mughal emperors and emperors have provided much evidence of architecture to India, which are witnesses of India’s original identity in today’s time. When we hear about Mughal architecture, we see huge buildings, buildings, forts, huge gates, huge halls, rooms, and minarets in front of us. The Mughal rule greatly enhanced the brilliant Indian arts in India with architecture, mosques, mausoleums and gardens.
Mughal rulers like Babur, Humayun, Akbar and Jahangir in India were known for spreading cultural development in the country. Much of the work in this area was done during the Mughal rule. The Mughal rulers were fond of culture; That’s why all the rulers were in support of the spread of education.
Mughal traditions greatly influenced the palaces and forts of many regional and local states. Almost all the rulers of the Mughal dynasty were great builders and have built magnificent monuments in India, which attract tourists not only from India but also from different places around the world.
The Mughal emperors had built fort gardens which add to the beauty of the buildings even today. The Mughal rulers not only built their own mausoleums, buildings, but unlike their predecessors, Akbar built a garden on the banks of the river, which is still established in the form of Mughal Garden architecture.
Babur was the first to set foot in India. He was a great scholar, he took the responsibility of building schools and colleges in his empire. He was very fond of gardens; That’s why he got many gardens constructed in the area of Agra and Lahore.
Nishal Bagh in Kashmir, Shalimar in Lahore and Pinjore Garden in Punjab were some examples of gardens developed during Babur’s reign and these gardens still exist today.
Babur was followed by his son Humayun who had a great love for books on subjects related to stars and natural features; He also got many madrasas built near Delhi, so that people could go there and learn.
Taj Mahal
One of the Seven Wonders of the World, a symbol of love, the Taj Mahal is not only the pride of India but also a wonderful testimony to the architecture of the Mughal rule. A white marble mausoleum, the Taj Mahal was built by Shah Jahan during the heyday of the Mughal dynasty to house the tomb of his favorite wife, Mumtaz Mahal.
Shah Jahan built this wonderful monument to dedicate the love and beauty of his beloved wife Mumtaz Mahal and to immortalize her name. Because of which this mausoleum is considered a symbol of love. The Taj Mahal is the mausoleum of Mumtaz Mahal, the third wife of Shah Jahan.
After the death of Mumtaz, Shah Jahan built the Taj Mahal in her memory. It is said that Mumtaz Mahal had expressed her desire to build a mausoleum while dying, after which Shah Jahan got the Taj Mahal built. It is said that the artisan was called from Bukhara city, he was expert in carving flowers on marble stone.
At the same time, skilled artisans living in Istanbul, Turkey were called to build the domes and skilled artisans were called from Samarkand to build the minarets. And in this way the craftsmen from different places had built the Taj Mahal. E. The construction of the Taj Mahal, which started in 1630, lasted for about 22 years. About 20 thousand laborers contributed in making it.
The monument is situated on the right bank of the river Yamuna from where it flows towards the east. It is spread over 42 acres. The Taj Mahal is made of white marble. There are four minarets in its four corners. Shah Jahan had called artisans from Baghdad and Turkey to make this wonderful thing.
It is believed that an artisan was called from Baghdad to make the Taj Mahal, who could carve curved letters on the stone. The terrain slopes from north to south of the Taj Mahal. The beauty of the Taj Mahal is enhanced manifold by the Taj Mahal Garden which is like the Garden of Paradise described in the Holy Quran.
The garden starts from the end of the main gate and is spread over an area of 300 meters. It ends near the mausoleum. Two marble canals with fountains near the garden cross the center of the garden, which are divided by stone-paved walkways with 16 flowerbeds.
The picture of supernatural beauty ‘Taj Mahal’ made of white stones on the banks of river Yamuna has made its identity not only in India but in the whole world. Thousands of tourists from distant countries come here to see this symbol of love.
JAMA Masjid
Jama Masjid is another architectural example located in Delhi. Jama Masjid is also known as the largest mosque in India. It was built by Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in 1656 AD. Historians say that 5,000 artisans built the Masjid-i-Jahan Numa or Jama Masjid on the hill Bhojal in Shahjahanabad. In the courtyard here, 25,000 people can offer their prayers simultaneously.
Both Hindu and Islamic styles were demonstrated in the architecture of this mosque in Old Delhi, which was built to replicate the Moti Masjid at the Red Fort in Agra. The legend also says that the walls of the mosque were inclined at a certain angle so that if an earthquake occurred, the walls would fall outwards.
This mosque is situated on the road opposite the Red Fort. This mosque is believed to be the last architectural work during the reign of Shah Jahan. Around 5000 artisans built the mosque with red sandstone and marble. Jama Masjid has four towers, two minarets and three gateways. The mosque has elaborate carvings and the Holy Quran is written on the wall.
The mosque also houses a collection of many things such as the Holy Quran, the relics of Muhammad, the red bear-hair of the Prophet, his footprints encased in a marble block. It took 6 years and about 10 lakh rupees to build this mosque. The north and south gates can be used to enter the Jama Masjid, while the eastern gate is open only on Fridays.
It is popular that Sultan used to enter Jama Masjid through this gate. Jama Masjid has 11 arches. The central arch is the largest, surmounted by a dome decorated with white and black marble. Every day hundreds of people come to Jama Masjid to offer prayers and to see it.
Red Fort
The Red Fort located in the country’s capital Delhi is not only the pride of India but it is also a wonderful specimen of Mughal architecture. The historically important Red Fort was built by Shah Jahan. Due to being made of red colored sandstone, it got its name Red Fort. Diwan-e-Aam, Diwan-e-Khas, Rang Mahal, Khas Mahal, Hamam, Naubatkhana, Hira Mahal and Shahi Burj are the memorable buildings inside it.
The Red Fort served as the capital of the Mughal dynasty during the reign of Emperor Shah Jahan. The fort has derived its name from the massive 33 meter high walls of red stone. In 1639, when the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan moved his capital from Agra to Delhi, the construction of the Red Fort was ordered by him in the north-eastern part of the newly founded city of Shahjahanabad. Present-day Shahjahanabad is known as Old Delhi. The construction took almost a decade to complete, and Yamuna water was used to feed the moat built around the fort.
The construction of Red Fort by massive red colored sandstone gave it the name Red Fort. Red Fort has two gates namely Lahori Gate and Delhi Gate. Emperor Shah Jahan used to hear the complaints of the common people in Diwan-i-Aam, Diwan-i-Khas as this was the name for his personal guests.
Rang Mahal was supposed to be the palace of the wives and mistresses of the emperor. The main attraction of Rang Mahal is a lotus shaped fountain which is made of a single marble. Other attractions of Red Fort are Moti Masjid or Pearl Mosque.
Sameer Shah Jahan’s private working area is Shahi Burj and Shahi Snan. The Red Fort now stands as a reminder of the grandeur and opulence of the Mughal dynasty. It took about 10 years to build the Red Fort.
It was built between 1638 and 1648 and was then named Qila-e-Mubarak. The importance of this fort made of red stone even today can be gauged from the fact that every year on August 15, on the occasion of Independence Day, the Prime Minister addresses the nation from the ramparts of the Red Fort.
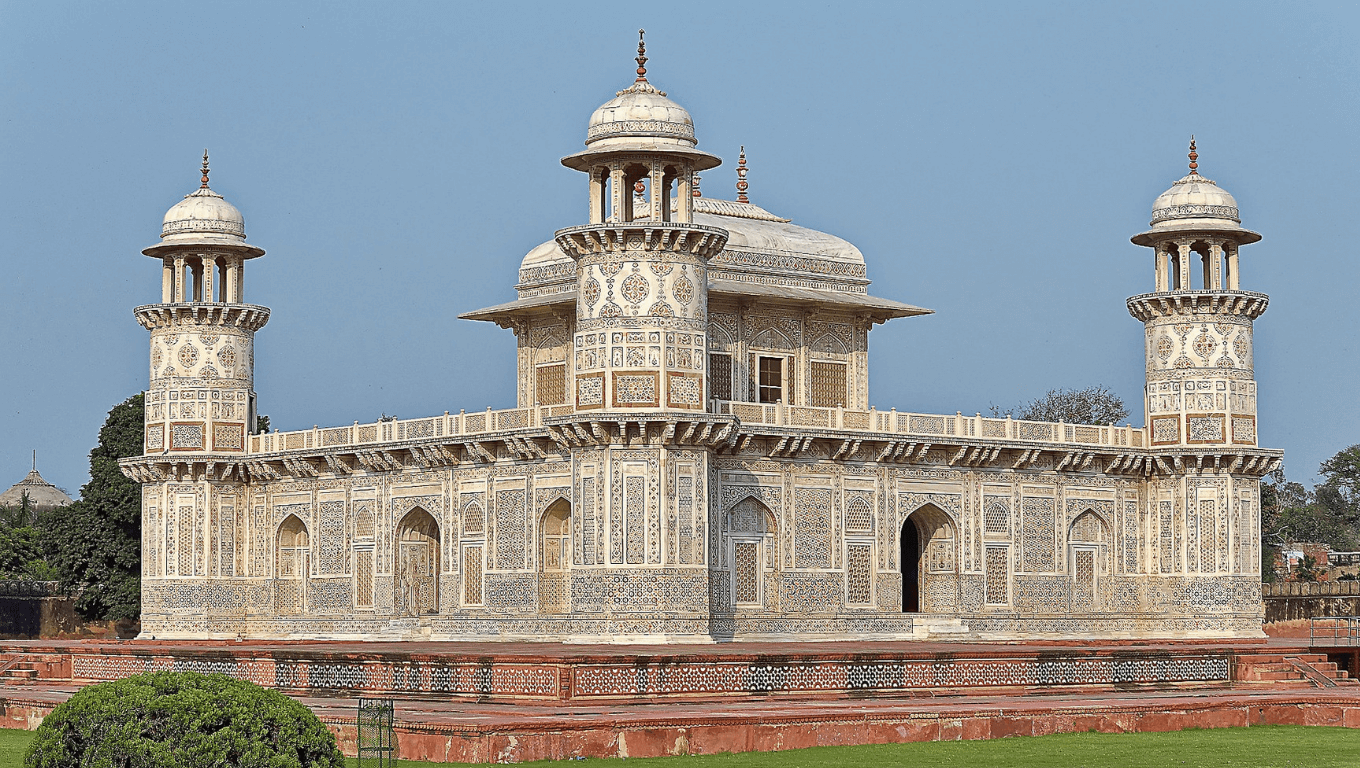
Itmad-ud-daulah
Itmad-ud-daulah is situated in the old city of Agra. Itmad-ud-daulah is the first marble mausoleum in India. This mausoleum belongs to Mir Ghiyas Beg, who was the vizier of the court of the Mughal emperor Jahangir. Jahangir had given the title of ‘Pillar of the State’ to his father-in-law Ghiyas Beg. Emperor Jahangir was in love with Nur Jahan, the beautiful daughter of Ghiyas Beg and wanted to marry her.
Nur Jahan built her father’s tomb in 1628 AD, about 7 years after his death. I got it done. This mausoleum is built in the middle of a garden in the Charbagh system, which stands surrounded by high walls on all sides. Standing on a raised sandstone platform, this mausoleum is made of white marble. The monument has a parallelogram central chamber which houses the tomb of the wazir and his wife Asmat Begum.
There are small cells around this room, in which there are graves of Noor Jahan and her first husband Sher Afghan’s daughter-Ladli Begum and other family members. A sandstone stairway leads to the first floor, where the mandapa above the central hall has a grand rectangular dome surmounted by two kalashas. This mandap is a plain marble grating without any engraving.
There are four round towers about 40 feet high on the upper four corners of this building, on which there are marble umbrellas. This Indo-Islamic monument is also known as the Jewel Box as it looks like a jewel box in the garden when viewed from the sky.
Itmad-ud-Daula’s tomb is famous for its rich multicolored ornamentation and carvings all over its surface. Bouquet, rose-water urn, grapes, wine cup and bottle have been freely used in the decoration scheme. The main floral elements are depicted mostly in the form of paintings in jar-shaped vases.
It is a matter of great interest that anthropomorphism has also been drawn in the plan of the painted blocks. The main gate of this mausoleum is in the eastern part, while ornate (pseudo) entrances have been constructed in the northern and southern parts. In the middle of the western part, there is a multi-storeyed and well-furnished building with many rooms, which hangs over the Yamuna. A shallow drain flows around the garden and the tomb, which was originally filled with water from two kandas located on the banks of the river. Tourists come from far and wide to see this tomb.
Humayun’s Tomb
Humayun’s Tomb is located in Delhi, it is the first example of Mughal architecture in India. In 1565, Humayun’s widow, Hamida Banu Begum, built the mausoleum for her dead husband nine years later. The Mughal Garden of Humayun’s Tomb is divided into four parts by walkways or running water.
The Mughal Gardens are built on the idea of the Garden of Paradise mentioned in the Holy Quran. It is believed that the construction of Humayun’s Tomb inspired the construction of the very famous Taj Mahal. UNESCO has given it the status of World Heritage. Humayun died in 1556 and his widow, Hamida Banu Begum, known as Haji Begum, started the construction of the tomb nine years after his death, which was completed in 1572.
Humayun had gained knowledge of the principles of Persian architecture and probably himself had planned this mausoleum. The mausoleum was built at a cost of 15 lakh rupees (1.5 million). Mirak Mirza Ghiyasbeg, a Persian architect, was commissioned by Haji Begum for this mausoleum.
This tomb is in the center of a square garden and the garden is divided into four main parts, which also have small ponds in the center. Made of red sandstone, the two-storied structure with fluted corners, stands on a 7 m high square plinth.
Humayun’s tomb is in the center of this complex. Many rulers of the Mughal dynasty are buried here. The last Mughal ruler, Bahadur Shah Zafar along with his three princes took refuge in this tomb during the First War of Independence (1857 AD).
This mausoleum is a mixture of Persian architecture and Indian traditions. Many rulers of the Mughal dynasty are buried here. The last Mughal ruler, Bahadur Shah Zafar along with his three princes took refuge in this tomb during the First War of Independence (1857 AD).
To see Humayun’s tomb, a gathering of tourists from all over the country as well as from abroad is here. This is the first mausoleum to use red stones while making it. In 1993 this mausoleum was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site and since then this mausoleum is famous all over the world.
Many small monuments are also built inside this tomb of Humayun, as soon as we enter the southern gate of the tomb, we see small monuments built on the way.
Tha (1531), the Battle of Chausa (1539), the Battle of Bilgram (1540) and the Battle of Sirhind (1555).
If you don’t take your private vehicle to these places then you can visit these Mughal Architectures by taking a Delhi taxi service .